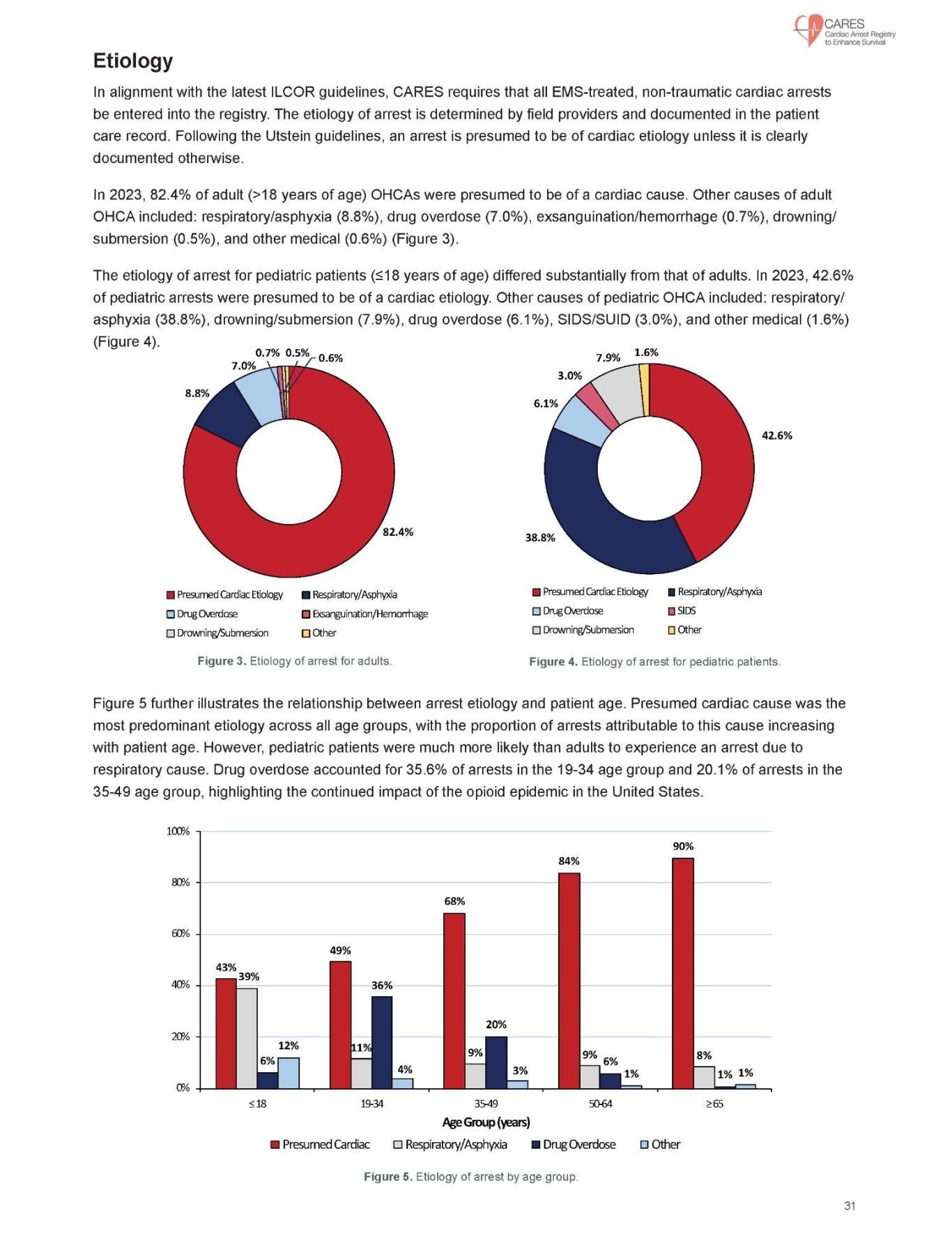
The ASAP CPR
(Adult Synergy Arrest Protocol)
Treatment Algorithms
AHA Approved for High Performance Teams
The Mission
Transforming Cardiac Arrest Response Training
Historically, the survival rates following out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) have averaged around 10%. However, since 2015, significant advancements in emergency cardiac care have emerged, leading to improved survival outcomes in real-world scenarios. We are currently at a critical juncture—a new benchmark in the management of adult cardiac arrest, firmly rooted in scientific research and positive patient outcomes.
There is a solution and we need to implement it. ASAP.
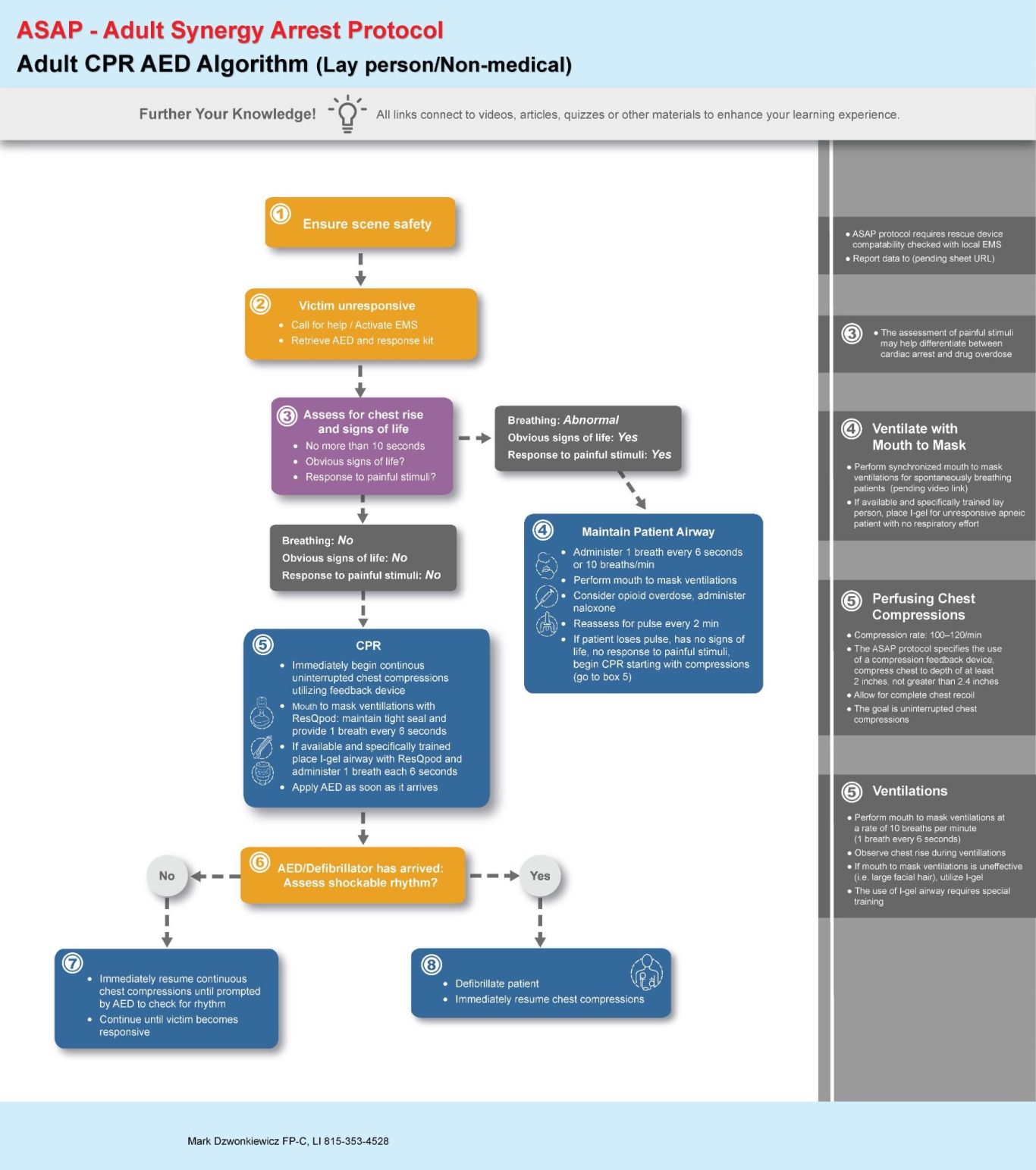
An Exceptional Specialty Course Experience
This is a specialized class. The algorithm presented here, when implemented correctly, is expected to surpass the performance of the current American Heart Association (AHA) resuscitation guidelines. To date, no interventions have proven to be more beneficial for survival from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) than those endorsed by the ASAP Protocols.
This assertion is unequivocal.
For further insights into some of the synergistic interventions recommended by the ASAP, please refer to the additional information below.
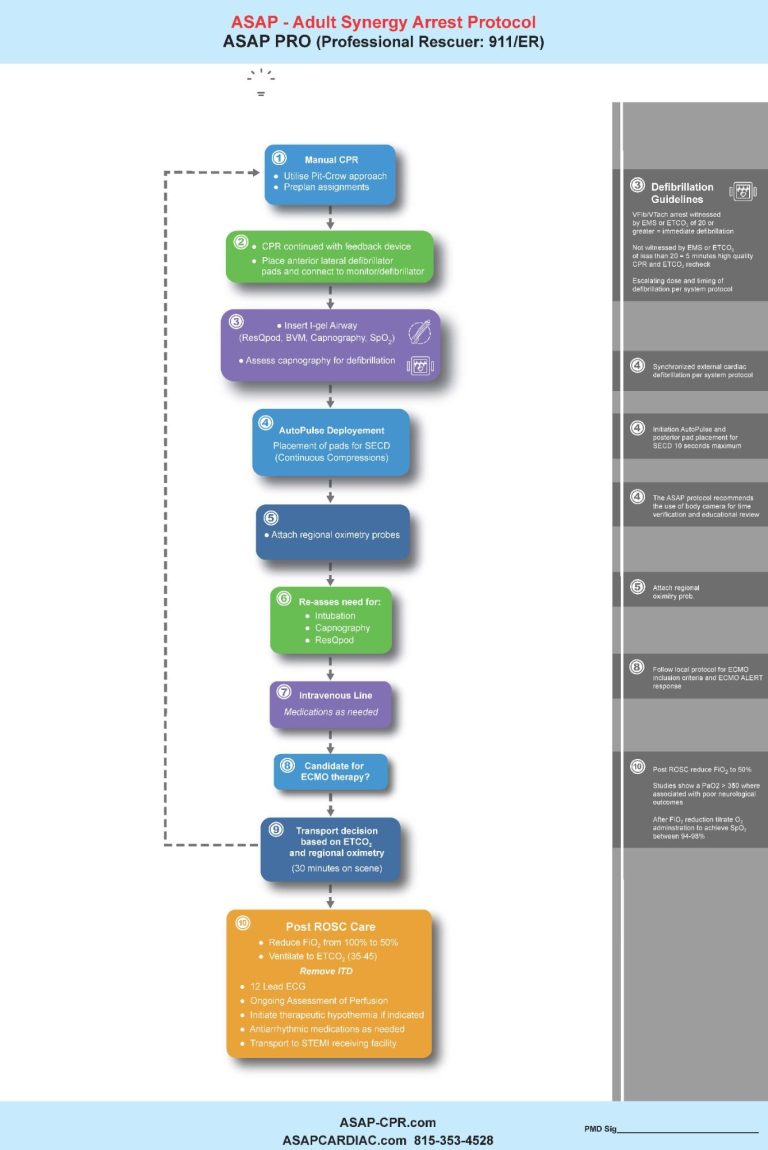
The I-Gel
The I-Gel has been recognized as the preferred initial airway adjunct within the ASAP Protocols due to its distinct characteristics and benefits.
The Lucas Device
The incorporation of the Lucas device significantly enhances the quality of chest compressions during cardiac resuscitation. This advanced mechanical apparatus ensures consistent and effective compressions, with its precision and operational efficiency contributing to improved patient outcomes. AHA Recommendations for Mechanical CPR DevicesCOR
LOE
Recommendations 2b C-LD
1. The use of mechanical CPR devices may be considered in specific settings where the delivery of high-quality manual compressions may be challenging or dangerous for the provider, as long as rescuers strictly limit interruptions in CPR during deployment and removal of the device.3: No Benefit B-R2. The routine use of mechanical CPR devices is not recommended.
The Res-Q Pod
The ResQPOD can:
- Double blood flow to the heart
- Increase blood flow to the brain by 50%
- increase survival from cardiac arrest by 25% or more
- Lower intracranial pressure (ICP)
- Increase cardiac output
- Improve neurologically-intact survival rates
- Double systolic blood pressure levels
- Increase the likelihood of successful defibrillation
to date, the AHA still does not recommend the use of the Res-Q-Pod
Saving Lives with Synergistic Interventions
Evidence-Based Approaches Demonstrated to Enhance Survival Outcomes in Real-World Applications.
At ASAPCardiac.com, we offer comprehensive educational resources, training videos, and foundational scientific knowledge to ensure that healthcare providers are well-informed, adequately prepared, and confident in implementing new life-saving protocols. Our materials are developed by experienced clinical educators and subject matter experts who are committed to a singular focus: the effective management of adult cardiac arrest.
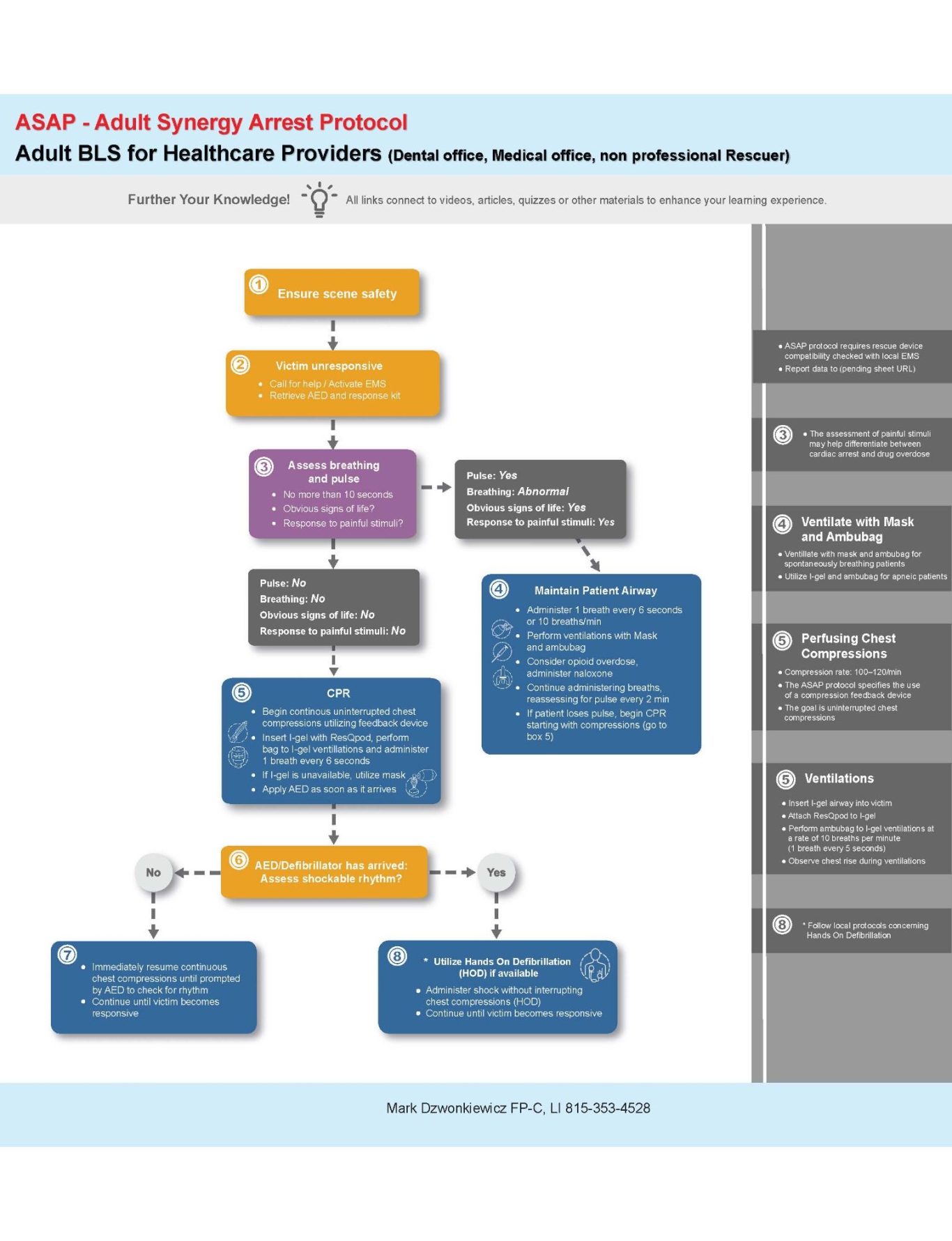
Professional resucers finally have the tools and traning nessesary to improve survival rates from OHCA.
We are excited to introduce the ASAP High Performance Team Training System, a comprehensive and straightforward training solution designed for use by any responding agency.
The ASAP HPT is a unique approch to treating the number 1 and number 2 causes of adult cardiac arrest.
Certification is awarded upon the successful completion of our online written examination.